High-Quality Multimodal Instrucion-Following Data and Human Preference Data
High-Quality Multimodal Instrucion-Following Data and Human Preference Data
Based on the LLaVA, we collect 10k human preference dataset with sampled input from 10k LLaVA-Instruct and output from LLaVA with temperature as 0.7.
| Data file name | File Size | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|
| human_preference_10k.json | 31 MB | 10K |
| vqav2_83k.json | 13 MB | 83K |
| aokvqa_16k.json | 4.9 MB | 16K |
| flickr_23k.json | 3.9 MB | 23K |
 LLaVA-RLHF: Aligned Large Language-and-Vision Assistant
LLaVA-RLHF: Aligned Large Language-and-Vision Assistant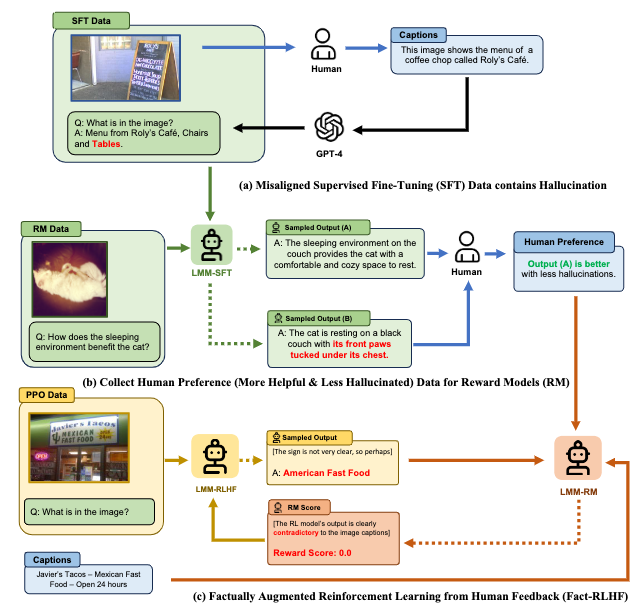
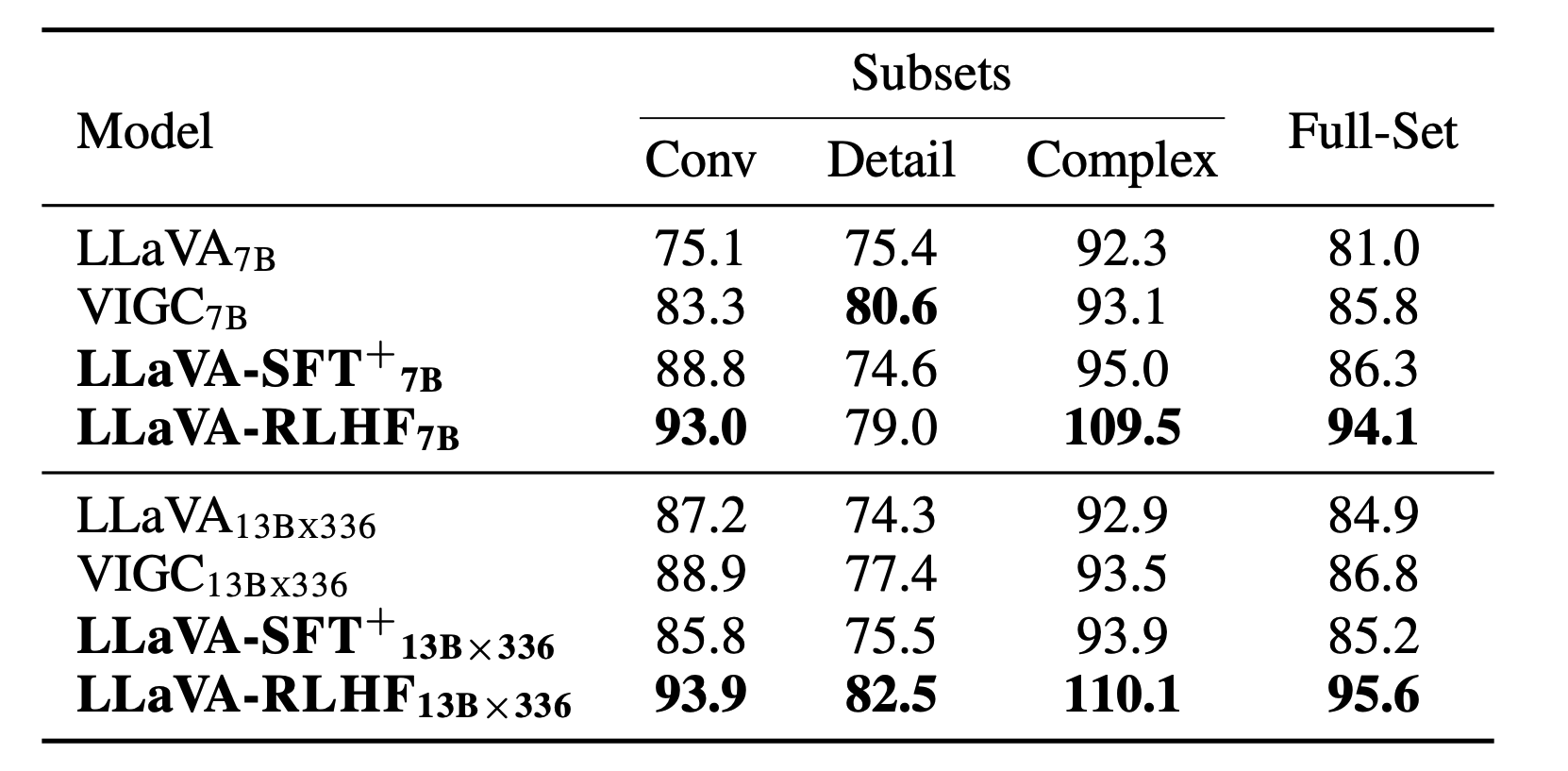
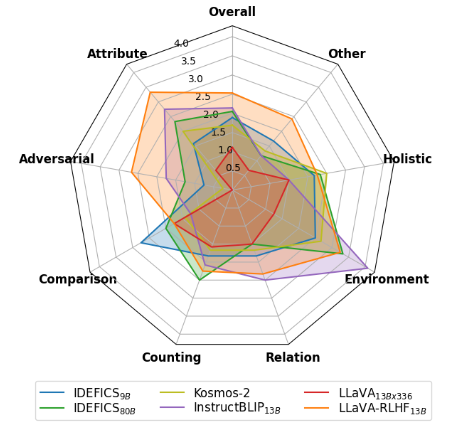
 Performance
Performance